How evictions work
The Eviction Process
Start here to learn all about evictions – common terms and what they mean, what happens in an eviction, and what you can do next.
The Eviction Process
Check our Resources and Legal Help pages for self-help guides, sample letters, and more.
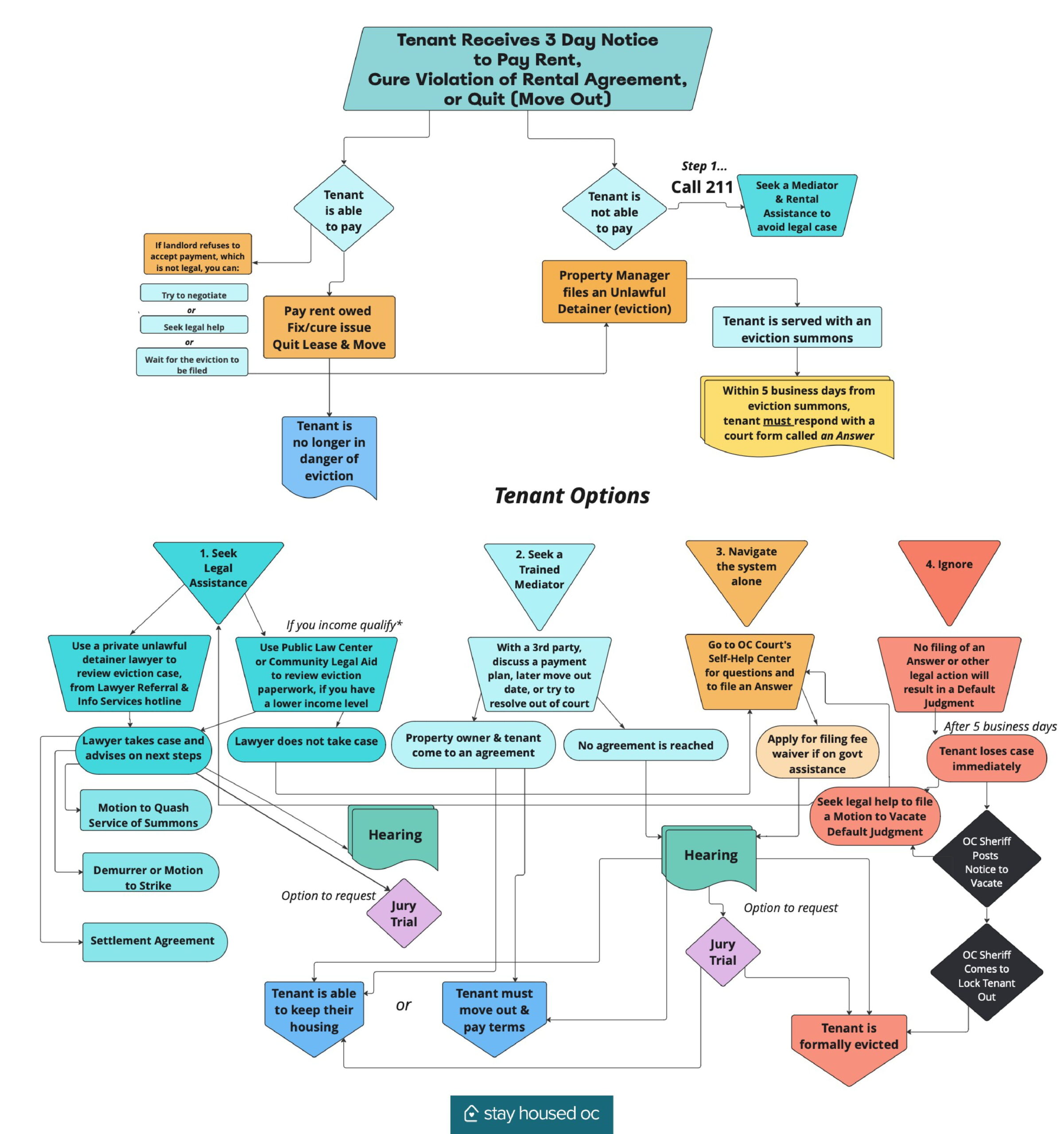
An eviction is a legal process between a tenant and a property owner. Eviction cases are called Unlawful Detainer cases.
The eviction process, for non-payment of rent, is very fast and can take just over a month.
An eviction can be filed for several reason such as:
- Not paying rent
- Illegal activity
- Not upholding the terms of the lease
- Staying after the lease expires (after being given proper notice)
- Foreclosure of rental property
- Taking the unit off the rental market
The eviction process is very fast and can take just over a month.
You have just 5 business days to respond to an eviction summons, if you have been personally handed the papers and been served.
If someone else who is not on the summons (such as a young family member) was handed the paper and served, you have 15 days to respond. This tends to be rare.
DO NOT IGNORE THE SUMMONS.
To respond, you need to file a responsive legal document called an Answer*, or a Demurrer or a Motion to Quash. Most people will file an Answer to respond.
You have 4 options:
- You can do it online
- You can file it after talking to the Self-Help staff at an OC court
- You can file the document in person at the courthouse
- You can get an eviction attorney to assist you
*You may file for a waiver of the filing fee if you are low income. Do not let finances stop you from filing. Click here for more info.
- Note: If you are receiving government aid (Medi-Cal, CalFresh, CalWorks, etc), you only need to fill out the top section of the Request to Waive Court Fees form (FM-001). Check the box #5a asking why you are filling the form out and mark the government aid you are receiving, and sign at the bottom of the form to have it processed.
- You will receive an Order on Court Fees Waiver (FW-003) telling you if your request was granted (approved) or denied. The Order will explain how to proceed. Act quickly – you only have 10 days from the date the Order is mailed to you to comply with the Order or exercise your options if your request was denied. Failure to act may result in the cancellation of any documents that you submitted.
There are 2 main types of evictions – No Fault Just Cause and At Fault.
No Fault eviction means you have done nothing wrong, but your landlord can ask you to move out for “no fault” reasons. You may receive a 60 or 90 day notice to vacate for this type of eviction.
Some no fault reasons include:
- If a landlord or their close family member wants to move into the unit
- If a landlord plans to take the unit off the rental market
- If a landlord plans to demolish the unit or make significant repairs for longer then 30 days
- To comply with court order or government agency
Since January 2020, many no fault just cause evictions related to a termination of tenancy have certain protections under AB 1481.
As of April 1, 2024, SB 567 is in effect for Orange County and the State of CA. Ordinances to meet or exceed SB 567 are already enacted in Buena Park, Costa Mesa, and Santa Ana.
At Fault eviction means your landlord says you have done something wrong. Some at fault reasons include:
- Nonpayment of rent
- Violating the lease
- Nuisance
- Damaging property
- Refusing to sign a new lease
- Committing a criminal act on the property
- Illegally subletting the unit
- Failure to give access
- Failing to vacate after tenant provided notice
A landlord must meet legal requirements before they can ask for a court order. This is a summary of the eviction process:
1. The landlord gives the tenant a written Notice to do something by a deadline.
For example, a Notice might say to pay rent or fix a problem by a certain date. The deadline can be 3 days or it can be months, depending on the issue.
2. The landlord starts an eviction case in court.
If the tenant doesn’t do what the Notice says by the deadline, the landlord can file an unlawful detainer lawsuit. The landlord must have a copy of the court papers delivered to the tenant named on the lease. These court papers are called an Evictions Summons or a Complaint. A tenant often receives both of these notices.
3. The tenant has 5 business days to file a response to the court.
- If the tenant is served with an Unlawful Detainer Complaint, the Complaint will show the court location and instruction on how to file the Response.
- Tenants have 5 business days from the date they were served to respond to the landlord’s Complaint and file their Response to the court.
- After the Response is filed by the tenant to the landlord’s Complaint and a “Request to Set Case for Trial” (form UD-150) is filed by the landlord, they will both be notified by mail of the time and place of the trial.
- If you disagree with what the landlord wrote in their request, you can file a counter-request. Use a Form UD-150 but check the box for “Counter-Request.”
- Have someone over 18 mail a copy to the landlord (or their attorney) and fill out the back of the original Request form.
- File the original and a copy with the court. Keep a copy for your own records.
- If the tenant doesn’t respond to the Complaint by the deadline, the landlord can file papers asking a judge to decide the case without the tenant’s input. If the tenant does respond, either side can ask for a trial where a judge or jury will decide. A tenant may ask for mediation help to negotiate the fees or the move out date.
- The court may enter a Default Judgment in favor of the landlord and issue a Writ of Possession after the 5th day if the tenant fails to file their written response with the court.
- There is no trial if a tenant does not file a written response to the Unlawful Detainer Complaint.
- The Default Judgment allows the landlord to obtain possession of the rental property.
4. The judge makes a decision.
If the landlord wins, they can ask the judge for papers that tell the sheriff to evict the tenants. The Sheriff will come out to the rental unit and post the “Notice to Vacate” the property on the resident’s door, giving the tenant a final five days in which to move out.
- The court may enter a “Default Judgment” in favor of the landlord and issue a Writ of Possession, if the tenant fails to file their written response to the court.
- There is no trial if the tenant does not file a written response to the Unlawful Detainer Complaint.
- The Default Judgment allows the landlord to obtain possession of the rental property. A Writ of Passion is a legal document that authorizes the Sheriff to physically remove and lock the tenant out of the property. The Sheriff will post a “Notice to Vacate” the property before enforcing the Writ of Possession. After the notice is posted, a tenant must move out within 5 days.
- If a tenant fails to move out within the 5 days, the Sheriff will physically remove the tenant and turn all of their possessions over to the landlord. The Sheriff’s cost for the eviction may be added to the eviction judgment, which the landlord can collect from the tenant.
- If you lose your eviction case, but you need more time to move, you can ask the court for a stay of execution. You will need to show the court that you have a good reason for needing more time. If you need more time to move out, you can ask for extra time by filing a Stay of Execution. You will need to pay your landlord for this extra time, so this is a rare occurrence. It is a good idea to bring the money to court when you ask for more time. A judge may allow you until the end of the day to provide the money. If you get a Stay of Execution, the judge will probably allow you to stay for up to 40 more days, but usually not longer. You will likely need a lawyer to help with this.
An eviction stays on the record for seven years. It may negatively impact your credit and your ability to secure future rental housing. If you have a minor child, it may impact their future consumer record as well.
Assembly Bill 1482, legislation that caps rent increases statewide and provides “just cause” eviction protections to tenants throughout California took effect January 1, 2020.
- AB 1482 applies to most residential rental properties in California. The law doesn’t apply to most single-family homes and condominiums, housing built within the last 15 years, and properties subject to a stricter rent control ordinance.
- AB 1482 does not apply to all renters. It protects many renters, but not all. The “just cause” protections apply to renters who lived in certain types of housing, like apartments, once they have lived in the unit for 12 months.
- For any tenant who is protected by AB-1482, the landlord must have “just cause” for eviction, including “at fault” reasons and “no fault” reasons.
- Tenants are entitled to relocation assistance for “no-fault” termination.
- Landlords are not required to give tenants a reason for termination of the tenancy if the tenant has been in the unit less than 12 months.
- Relocation assistance should be equal to one month of rent at least or may waive in writing last month’s rent.
- Tenants should receive a 30-Day Termination Notice if they have lived in the unit less than 12 months. After being in the unit for more than 12 months, tenants are entitled to receive a 60-Day Termination Notice with “just cause”.
- The notice should be delivered in person, posted, and/or mailed. Your landlord cannot text or email this notice.
- Single-family houses are exempt from AB 1482 and a landlord isn’t obligated to give a reason to vacate. After being in the house more than 12 months, the landlord would need to serve the tenant with a 60-Day Termination Notice.
🎦 Watch Videos on the CA Eviction Process
Glossary of Terms
Here’s a list of words you will often see in the eviction process, and what they mean.*
is used when the landlord thinks their tenant is behind on rent. It’s asking the tenant to pay the back rent or move out (quit).
concerns a party’s right to amend a pleading filed in a court action. The court can decide on whether a party may add or remove the name of a party, or correct a mistake in a pleading. Additionally, the court may alter the time for response of the opposing party.
a motion to set aside and vacate a judgment and enter another and different judgment in CA is very useful where it is fairly obvious that a judgment or decree is incorrect or erroneous in some way that materially affects the substantial rights of the moving party.
California Code of Civil Procedure (CCP) § (section) 663 has no time restrictions as CCP §473 does; however, the aggrieved party must demonstrate the court’s decision was based upon an incorrect or erroneous legal or factual basis.
an affidavit is the written version of swearing under oath to tell the truth, just as if you were testifying in a courtroom.
an answer is a reply to a question or a solution to a problem. In law, an answer refers to a defendant’s first formal written statement to a plaintiff’s initial petition or complaint. This opening written statement will admit or deny the allegations, or demand more information about the claims of wrongdoing.
an appeal is when someone who loses a case in a trial court asks a higher court (the appellate court) to review the trial court’s decision.
in CA, there is no legal definition for “unsafe” living conditions. Generally, the rule of thumb is that if your living environment affects your health or safety, then it can be considered an “unsafe” living condition.
an eviction complaint is a legal filing made against one party by another in order to attempt to legally evict the first party from property owned by the second party. The paperwork for this filing makes up the “complaint” and typically indicates the names of both parties and the physical address from which one party is trying to evict the other. It will also indicate the reason for the eviction.
the tenant decides to do what the notice that they are given says, which is usually to pay rent or quit (leave the unit).
a continuance is the postponement of a hearing, trial, or other scheduled court proceeding at the request of either or both parties in a legal action. Parties in a suit or the judge themselves may wish to have a continuance granted in order to prepare for proceedings.
a court clerk prepares and issues orders of the court (summonses, and other official documentation), preparing dockets of cases, examine legal documents submitted to courts, searching files and contacting witnesses, attorneys or litigants to obtain information for the court, preparing staff schedules, swearing in jury members, interpreters, witnesses or defendants, instructing parties about the timing of court appearances. *Documents need to be sent to the court clerk to be filed.
a default judgment is a judgment against a defendant who fails to answer a lawsuit. If a person or entity is sued and ignores the lawsuit entirely, the person or entity suing has the ability to get a judgment upon meeting certain criteria.
a demurrer is a legal objection to the sufficiency of a pleading, attacking what appears on the face of the document and seeking dismissal of a case against the defendant. The demurrer must be made in open court before a plea is entered unless the court allows it to be made at a later time.
a department is what the rooms are called in a courthouse.
a deposition is taking a witness’ testimony outside of court. At a deposition, the witness is sworn in, and answers questions under penalty of perjury. A court reporter is hired to transcribe the testimony.
is how you gather the evidence you will need to prove your case. Discovery is best described as a process where each side tries to find out what the other side is going to use at trial to support the claims made in the Unlawful Detainer lawsuit. Both sides to an Unlawful Detainer lawsuit have the right to conduct discovery.
a docket is a log containing the complete history of each case (including what happened in court) in the form of brief chronological entries summarizing the court proceedings. Every case is assigned a unique docket number.
refers to a legal principle that prevents someone from arguing something or asserting a right that contradicts what they previously said or agreed to by law. An estoppel prevents one person from contradicting an action or statement from the past.
evidence is any proof legally presented at trial through witnesses, records, and/or exhibits.
court filings are eliminated from the record and can never be retrieved or reopened.
a fee waiver is a full or partial release from the requirement of payment of a fee and from any provision in lieu of fee payment.
*Fees can be waived if on government assistance such as Medi-Cal, CalWorks, CalFresh, WIC, Unemployment, etc. by filling out a form (fee waiver form FW-001)
reviews what is going to be presented at trial and to access what will be needed at trial, e.g. an interpreter, trial notebooks, etc. This is done in front of the judge. This is mandatory for attorneys but not for their clients.
a form Interrogatory is a list of questions on a court form. You are sent these by the Plaintiff in a case where the Plaintiff propounds discovery.
a FW-002 is a form to Request to Waive Additional Court Fees (Superior Court). This form asks the court to waive additional court fees that are not covered in a current order.
a hearing refers to any formal proceeding before a court.
an intake is usually the first contact with a law office where the office accesses a client’s case and gathers information.
an interrogatory is a list of questions one party sends to another as part of the discovery process. The recipient must answer the questions under oath and according to the case’s schedule.
a judgment is when the judge makes a decision in an eviction case. The judgment may happen after a trial or, it may happen without your input if you didn’t file an answer.
is a case where the amounts in question are between $10,000 and $25,000.
a person who is involved in a civil legal case, either because they are making a formal complaint about someone, or because a complaint is being made about them.
stands for meet and confer
encourages parties in a case to settle their matter in whole or in part. It happens at the courthouse. Accordingly, all parties must attend this court appearance. This means that both sides of a case have to meet and talk and try to work things out regarding all the issues IN PERSON.
requires that parties meet and confer in a “reasonable and good faith attempt at an informal resolution of each issue presented by the [discovery] motion.” This means that both sides of a case have to meet and talk and try to work things out regarding all the issues brought up by any pending motion.
a motion is a legal tool that asks a judge to make a decision.
a summary judgment motion is not a substitute for trial, it is a tool that allows courts to weed out cases that do not need a trial to be resolved. It also allows the court to simplify and streamline the case so that trial is more efficient and focused on the areas of actual dispute. It can be used by either side to get rid of certain aspects of argument/contention so they are not argued at trial.
is a date for the hearing of a motion that is assigned by the court clerk. (BEFORE you can complete your moving(motion) papers, or have them served and filed to the opposing party, you need to get a hearing date assigned by the court. Tell the clerk what type of motion you are bringing, and when you want to have it set. Make sure you choose a date that is far enough away that you can give the other sides the required notice of the hearing.)
a motion to vacate specifically asks a judge to cancel something.
stands for motion for settlement conference
stands for motion for summary judgment
requires the prevailing party on any motion to give notice of the court’s ruling to all other parties or their attorneys unless notice is waived by all parties and is entered in the minutes. It starts the clock on how many days an appeal can be filed.
this is a notice that the Sheriff serves to a tenant or residence which states the date that the Sheriff will come back to remove the occupants and lock them out.
stands for Notice to Vacate
In CA, when a tenant becomes what is often loosely defined as a “nuisance,” the landlord has the right to oust them from the property upon serving up a 3-day notice for eviction. This action is legally called “Termination of Tenancy Based on Nuisance.”
stands for opposing counsel
is the attorney for the other side of your case.
to testify falsely, or to give false or misleading testimony, may be perjury.
are any motions that are filed after a decision by a judge. There are several different types of post-judgment motions, but the most common are motions for a new trial, motions to vacate, and motions to set-aside.
to preserve a jury is to ask for a jury trial at the time you answer your unlawful detainer.
the proof of service affidavit states the party who served the documents, what documents were served, the method of service, and where the document was served.
means that you are acting as your own attorney.
stands for Request for Admissions.
Santa Ana’s Rent Stabilization and Just Cause Eviction Ordinance is a local law that sets a maximum annual rent increase and provides tenants protections from evictions without just cause.
is a discovery device that allows one party to request that another party admit or deny the truth of a statement under oath. If admitted, the statement is considered to be true for all purposes of the current trial.
when improper conduct is employed during litigation. Sanctions are usually fines. A lawyer seeking sanctions must file a motion with the court. A hearing is set during which the lawyer must produce evidence of wrongful conduct.
records are made unavailable to the public, but may be reopened. CA automatically seals any case that does not result in a judgment for the landlord. The state further provides automatic sealing for all other cases unless the landlord wins within 60 days. Records may be unsealed after 60 days if the landlord won at trial and can demonstrate extenuating circumstances.
are questions that are typed up by the opposing party or their attorney. This will be a numbered list of questions that the opposing side asks you to answer. It can be no more than 35 questions long. Each numbered question is called an interrogatory. “Interrogatory” is a legal word meaning “question.”
a stipulated judgment has similar effects as a regular judgment, but the main difference is the debtor agrees to gives up essential rights: The debt collector isn’t required to prove you’re responsible for the alleged debt. You give up any defenses you can use against the creditor, such as the statute of limitations.
a summons is a court form which notifies the defendant that they are being sued and lists the day the defendant needs to appear in court (the Return Date).
to testify means to give one’s testimony under oath as a witness; to give evidence as a witness.
Statement of the Case, Witness List, Exhibit List, Jury Instructions, Photographs and Reports – Must be filed and served 5 court days before trial.
A three ring binder with a Table of Contents and Tabs that has a LIST.
is an eviction proceeding. The cause of action of an unlawful detainer is that the possession was originally lawful, but turned unlawful only upon the expiration of the right to possess. To show that the possession was initially lawful, the basis of such lawful possession must then be established.
to ‘waive’ is to forego something. It is an act of voluntarily giving up a right, and can apply to a variety of legal situations including knowingly giving up a legal right such as a speedy trial, a jury trial, giving up some rights in a settlement talk, or not enforcing a term of contract. A landlord can waive a right a lease has given them to collect a late fee, for example.
when a court dismisses an action, they can either do so “with prejudice” or “without prejudice.” Dismissal with prejudice means that the plaintiff cannot refile the same claim again in that court.
when a court dismisses an action, they can either do so “with prejudice” or “without prejudice.” Dismissal without prejudice means that the plaintiff can refile the same claim again in that court. This usually happens when the dismissal is based on a technicality.
witness and exhibit lists are critical as they represent the evidence that will go in front of a jury at trial.
a writ is an order issued by a legal authority with administrative or judicial powers, typically a court. A petition for a writ explains to the appellate division what happened in the trial court, what error you (the petitioner) believe the trial court made, why you have no other adequate remedy at law, and what order you are requesting the appellate division to issue.
*Adapted from the Eviction Defense Network LA (EDN)